Ever since the rebellion in the garden of Eden that sowed seeds
of distrust against God and his word, there have been two groups of
people: those who believe and obey the word of God and those who don't.
Among those who don't believe it has become quite fashionable to smirk
and be amused at the quaint beliefs of those bible believing
unsophisticates - until of course - evidence for those beliefs are
found and confirmed. Here is the typical sequence:
1. A pronouncement is made that directly
contradicts the bible - such as "King David didn't exist because no
archeological evidence can be found confirming his existence."
2. Bible doubters jump on the band wagon and poke fun at those quaint
bible believers - until evidence is found that confirms the Bible. In
the case of King David, it was the
Tel Dan Stele, a
monument erected in the 8th or 9th century BC by one of the kings of
Aram (ancient Syria) which bore the inscription "...of the House of
David..."
3. An acknowledgement is made that the Bible was right
(again) and off they go looking for some other part of the Bible to
doubt.
In the case of King David, all but the most obstinate doubters will agree with the myth hunters:
"When the inscription at Tel-dan was found, that put the debate to rest. It was clear that David did exist."1
Today, one of the Bible truths most attacked by scientists in every field is the Bible's proclamation that the entire universe was created in 6 days. This proclamation is strongly denied because if true, it means that neither the Big Bang nor Darwinian evolution can be true, because both of those require billions of years. Therefore atheistic and materialistic scientists have a vested interest in keeping belief in a billions year old universe alive - it's required for their worldview. And thus they take every opportunity to promote that godless belief. And so we regularly see such scientists either outright mocking Christian belief, or attempting to show why, according to their calculations, it cannot be correct. Here is one of those attempts made during the reboot of Cosmos, as narrated by the show's host, Neil deGrasse Tyson:
"The crab nebula is about 6,500 light years from earth. According to some beliefs that's the age of the whole universe. But if the universe were only 6,500 years old, how could we see the light from anything more distant than the crab nebula? We couldn't. There wouldn't have been enough time for the light to get to earth from anywhere farther away than 6,500 light years in any direction. That's just enough time for light to travel through a tiny portion of our milky way galaxy.
"To believe in a universe as young as only 6 or 7,000 years old is to extinguish the light from most of the galaxy. Not to mention the light from all the hundred billion other galaxies in the observable universe."2
This actually points to a bigger problem - the problem of distant starlight. And what the Big Bangers won't tell you is that the Big Bang has its own distant starlight problem. I dealt with the distant starlight problem in the article "Which theory has the fatal flaw, Big Bang or Creation", so I won't cover that ground again here. In this article we'll focus instead on the problems with the big bang proclamation of a 13.75 billion year old universe3.
As far as such scientists are concerned, people who believe in a 6,000 year old earth are like believers in a flat earth - hopelessly backwards and foolishly ignorant. But there is an important distinction to be made here. Believers in the Bible are not like believers in a flat earth. Besides the fact that the bible proclaimed the earth is round thousands of years before 1492 when Columbus sailed the ocean blue,4 there is direct, clear evidence that the earth is round: photographs of the earth from space being one of them. This site is about rational reasons to believe, so for those really seeking the truth, that should be the end of the matter.
Now that we've established Christians believe because of strong, direct, evidence supported reasons, let's apply the same standard to the age of the earth. Let's have the scientists present direct, clear evidence that the universe is 13.75 billion years old as they claim. Direct evidence would be something like a clock that has been running since the beginning that we could consult, or an eye witness that existed for the duration that can give testimony as to the passage of time or the time frame.
Scientists will say something to the effect "a clock running since the beginning - that's absurd. That would require the clock to exist in the beginning before anything existed which is clearly impossible. Likewise, a testimony would require an immortal being outside of time and space - which is also impossible." So scientists have no direct, conclusive evidence of a 13.75 billion year old universe. What evidence do they have? Let's come back to that question. First, let me point out that we do have an eye witness testimony of an immortal being outside of time of space - that of God who said:
"For in six days the LORD made the heavens and the earth, the sea, and all that is in them, but he rested on the seventh day."
Ex 20.11
Scientists of course do not accept that testimony- it's not scientific. But please note that the Bible describes God as having the needed qualities: scripture testifies that God is both immortal (1 Tim 1.17,) and existed before any created thing, and thus is outside of space and time (Gen 1.1, John 1.1-3). (Note - scientist agree that space and time were both created - though they believe they were created in the Big Bang).
So Christians have the direct evidence of the God of Creation who testifies as to how long it took him to create the universe: 6 days. Scientists have no direct evidence of a 13.75 billion year old galaxy. So let's return to the question above: exactly what evidence do they have as to the age of the universe?
How Scientists Calculate the Age of the Universe
Since scientists cannot consult clocks to determine the age of the earth, and they can't use tools like the much abused and misused radiometric dating process as they do for materials on earth. Since the stars they want to measure are light years away, they have no physical samples to work with. What then, do they have to work with? The only thing they have to work with is the light itself from the stars. That's it. How can such light tell them the age of the stars? It can't -directly. Scientists make estimates based on two basic qualities of the light: Brightness and red shift. For determining age by brightness, they quantify the brightness and then they relate that to distance from the earth. Then using the speed of light, they determine how much time it would have taken light to traverse that distance. Finally they add the supposed age of the star. For determining age by red shift, they relate red shift to the expansion of space. They then estimate how much the universe has expanded since the big bang, then calculate backwards to the big bang. Or as NASA put it:
Astronomers estimate the age of the universe in two ways: 1) by looking for the oldest stars; and 2) by measuring the rate of expansion of the universe and extrapolating back to the Big Bang; just as crime detectives can trace the origin of a bullet from the holes in a wall.5
In looking for the oldest stars they're looking for the dimmest (least bright stars). In attempting to measure the expansion of the universe, they look at red shift. So they're looking at brightness and red shift as noted above.
Flaws in the calculations of the age of the universe
So the primary tools of the astronomer uses in
guessing age is brightness (or magnitude) and red shift. But
making the transition from brightness and red shift to age is plagued
with either guesswork or contradictory evidence as the closer look below
demonstrates.
Determining Star Age by Brightness:
As NASA states, the goal is to find the oldest stars, because the
universe would obviously have to be older than that. The process
works like this: There is a direct correlation between the star's color,
and its brightness, or as one source put it:
"It turns out that a star's color spectrum is a good indication of its actual brightness"6
Thus by measuring the star's colors, they can gauge it's actual brightness. Then all they need to do is calibrate the brightness (which dims with distance) to the actual distance. To do that scientists started with an actual measurement of nearby stars using a method similar to that which produces a 3D image in a movie theatre. 3D movies are made by taking two pictures from cameras slightly separated. (The reason you're given glasses is to make sure each eye sees only the images taken from that eye's angle or perspective.) The difference in the angles caused by these parallax inducing views of the same object is used by the brain to create a 3D image. The brain is able to calculate the relative distance between the various objects in view - which are seen at slightly different angles - and gives you the appropriate 3D perception. (That process, by the way involves information coded into the brain. Something that complex - involving the interpretation of electrical signals to produce a 3D picture - could not have evolved.) In the same manner, scientists take pictures of the same star 6 months apart. The pictures are taken with the earth having traveled halfway through its orbit and thus they are taken at a slightly different angles allowing scientists to use trigonometry to calculate the distance to the star. Once they have the distance to the nearest stars (those being no more than 400 light years from earth) and their colors and apparent brightness , they can then correlate that to those of more distant stars.
So using that technique, they go looking for the dimmest stars, which to scientists means the most distance stars. This in turn means the light has been traveling longest, and thus they're also the oldest stars. But there are at least two problems with that approach7. There's also a problem with the red shift method of age determination. We'll look at all three problems next.
Problems with the brightness method of Star age determination
Problem 1. Great distances mean great
errors.
Just as trying to shoot a target with a gun over distances of multiple
miles gets increasingly difficult the more distant the target, so
estimating the distance to dim stars gets increasingly difficult the
more distant and dim the star. As NASA put it:
The uncertainty in this estimate is due to the difficulty in determining the exact distance to a globular cluster (hence, an uncertainty in the brightness (and mass) of the stars in the cluster).8 [emphasis mine]
Obviously the problem compounds introducing
further guesswork as they look for older, even dimmer stars.
Problem 2. Ignorance of how Stars form
Scientists have no idea how stars form using using regular baryonic matter9 (the stuff you and I are made of). As one scientist put it:
"The silent embarrassment of modern astrophysics is that we do not know how even a single one of these stars managed to form."10
Or to quote NASA again:
"Another source of uncertainty in this estimate lies in our ignorance of some of the finer details of stellar evolution. Presumably, the universe itself is at least as old as the oldest globular clusters that reside in it.11 [emphasis mine]
Do you see a problem here? There are at least two: Scientists are trying to determine the age of the universe by adding two unknown quantities. They have no idea how stars form, yet they add the "age of the star" to their calculation. How can they know its age if they don't know how it forms? They also have a very difficult time determining the exact distance to the star. Nevertheless they guess at a distance so they can calculate an age based on the time it would take light to traverse that guessed at distance. So by the brightness method we get an age based on an unknown quantity and a very difficult to measure quantity. If this sounds like an inaccurate method - you're right, it is. As one article notes:
"In fact early measurements of distances were wildly off."12
Thus they must use other methods to compare and adjust this method. The other primary measurement they make for star age is also not a measurement of time, it's a measurement of red shift, and that has its own problems.
Problems with the Red Shift method of Star age determination
Problem 3. Contradictions to Hubble's Law
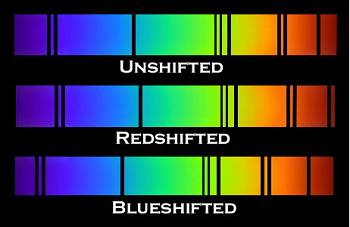
We're all familiar with how the sound of an approaching siren has a higher pitch, and the sound of a receding siren has a lower and decreasing pitch. this is due to the effect of motion on the sound waves which compresses (for approaching vehicles) or stretches (for receding vehicles) sound waves in a quite noticeable fashion. This is called the Doppler effect. The Doppler phenomenon also effects light waves - the difference being approaching light is blue shifted and receding light is red shifted.
Thus a red shifted star can be interpreted as moving away from us. But there's another way to achieve the same effect without moving the object - That's by increasing the space between the object and the observer. This gives an apparent motion to the observer though technically - the object is not moving - it remains stationary while space is inserted between the object and the observer. This is called Cosmological red shift. Cosmologist propose this type of expansion of space to get around the observation that almost all stars appear to be receding from us - which would put us in the center of the universe.
That observation was made by Edwin Hubble when he noticed that almost all galaxies were red shifted; and the furthest ones had the greatest red shift and thus were moving fastest. Put another way - the more red shifted the galaxies were, the further away they are and the faster they're receding from us. To Hubble, an atheist, that idea was abhorrent to him. That is not the outcome of a random big bang explosion, that is the careful placement of a thoughtful designer.
To get around the obvious conclusion that earth is in the center of a purposefully designed universe, cosmologists posit that red shift (as measured by spectral lines - see the top image) is due not to the Doppler effect - that is the object moving through space; but is instead due to the cosmological factor - space being inserted between the observer and the object, or as they call it - the expansion of space.
Thus determining age by red shift is based on the assumption that Hubble's law is true, and red shifts are understood as an expanding universe moving objects more distant from us (and from each other) when seen in objects outside our galaxy. Dr. John Hartnett summarizes how materialist cosmologists understand the implications of Hubble's law as follows:
"In other words, all the extra galactic red shifts are due to the expansion of the universe."13
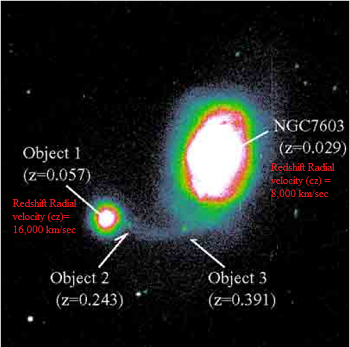 |
An
Exception to the Hubble Law The main galaxy, NGC 7603 is an active, X-Ray bright Seyfert with a redshift of 8,000 km/sec. The companion is smaller with a redshift of 16,000 km/sec and a bright rim where the filament from the Seyfert enters it. The recent measures indicate the filament is drawn out of the low redshift parent and contains the two emission line, high redshift, quasar like objects. From López-Corredoira and Gutiérrez 2002.
Caption
by
Halton Arp |
Thus by running the scenario backgrounds, you could calculate how much time it took to get to the present location. But is that interpretation of red shift true? Eminent scientist and astronomer Halton Arp, disagrees. He suggests high red shift are indicative not of large distance, but young age14. Arp has identified many pictures of galaxies that don't fit the "red shifts are due to the expansion of the universe" scenario. For providing such data contradictory to the big bang, he was banned from any further observatory time. Before being banned, he identified many examples of contradictions to the Hubble "law" such as Seyfert galaxy NGC 7603 (above) which has a small companion galaxy next to it. The large main galaxy has a red shift of 8,700 km/sec while the smaller one has a red shift of 17,000 km/sec - a great difference. This should mean that the galaxies are very far apart - remember the greater the red shift, the greater the speed and distance. Yet Arp has demonstrated that not only are they close, there are bridges of materials that connect the two. Thus Hubble's law does not apply in this instance. And there are many others like it. It is evidence such as this which have caused some physicists to doubt this interpretation of red shift data:
"In my view the general acceptance of these ideas and the subsequent edifices of the models which have been erected around these ideas is a fundamental mistake. The direction that research will take in the 21st century, however, may well lead to a compounding of that mistake, and I predict no immediate return to reality.15
Geoffrey Burbudge, theoretical astrophysicist 2001
Or as physicist and cosmologist Dr Hartnett puts it:
"This brings into doubt the whole Hubble law regime upon which big bang cosmology hangs"16
Thus the whole approach to dating the universe using red shift is suspect, including:
- The Hubble Law
- The supposed expansion of the universe
- And with these two disqualified, any calculations of age based on them are also disqualified.
Add to that the evidence that the universe appears young and you see a pattern begin to emerge. A pattern of denial of the obvious. When scientists send probes, they discover many objects look young - though they should look old and scarred if really billions of years old. Venus looks so young it appears "freshly minted,"17 Saturn's rings are clearly young18, and like Venus, Pluto likewise appears young.19 Indeed the entire solar system appears to be young. Yet since scientists are highly invested and tightly bound to the big bang theory which says the universe must be billions of years old, they simply cannot accept what the evidence is plainly telling them. And so they make up stories about why things look young like "Venus' surface must have recently been resurfaced to look so young." Thus some scientists aren't interested in fitting the theory to the data; they already have their theory and they're not changing it. So instead they fit the data to their theory - however twisted it becomes and regardless of the number of hypothetical entities they have to add like dark matter and dark energy.
Conclusion
Materialist scientists want you to think their estimate of the age of the universe is as solid as the timing of an Olympic event, but when you look underneath the hood at their timing mechanisms, what you find are not precise measurements, but guesses based on "wildly" inaccurate estimates, ages based on ignorance, and ages based on evidence that contradictions the basic theory they're trying to affirm. Thus when scientists categorically state "the universe is 13.75 billion years old" what they are categorically affirming is not a measured time, but their commitment to their faith in the big bang theory - regardless of glaring contradictions and inaccuracies. If they want to support wild speculation, that's their prerogative, but they shouldn't pass it off as settled science.
13.75 billion years as the age of the universe
is neither a settled fact or even good science; nor is it a silver
bullet with which to slay young earth creationism. It is merely a
statement of faith in a disqualified theory: the big bang.
Scientists would like to use that number as a shield against
Biblical truth, but this shield is full of holes and so offers no
protection against either biblical truth, or the abundant evidence
of a young universe. Do not be deceived: materialist
scientists would have you believe they have the certainty of
precisely measured time when all they have are guesses based on
ignorance, wildly inaccurate estimates and contradictory evidence.
That is not how good science operates. And 13.75 billions years is
not a statement of scientific fact. It is a statement of faith -
based on bad science and selective evidence. Need I point out that
arguing
from ignorance, and
selective evidence are logical fallacies?
Duane Caldwell | posted 10/20/2015
Follow @duanecaldwell
Notes
1
Myth Hunters episode "The Real King Solomon's Mines" TV
Documentary, 1/09/2014,
back
2 Cosmos: A Space-Time Odyssey: Episode 4 "A
Sky Full of Ghosts" 3/30/2014 TV - Documentary
back
3 13.75 billion years is the age of the universe
as published by Edward L Wright at UCLA, +/- 0.1 Billion years.
Age of the Universe
http://www.astro.ucla.edu/~wright/age.html
back
4 The prophet Isaiah,
speaking of God, proclaimed:
"He sits enthroned above the circle of the earth," (Is
40.22)
Isaiah prophesied from 740 to 680 BC (Gleason Archer, Expositors
Commentary, Vol 1, p. 371). Thus the bible proclaimed the earth was
circular and not flat 2 millennia before Columbus made his voyage.
back
5
NASA - WMAP - Age of the Universe How Old is the
Universe?
http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/uni_age.html
accessed 10/15/2015
back
6.
How are astronomers able to measure how far away a star is?http://science.howstuffworks.com/question224.htm
accessed 10/18/2015
back
7 Aside from the two highlighted, there's also the
issue of the assumption that the one way speed of light (in bound to
earth) is the same as the two way speed of the light. The Anisotropic
Synchrony Convention proposes that the solution to the distant starlight
problem is in the speed of light: The average over a round way trip is
indeed constant as measurements show, but the speed of the individual
legs varies, but when averaged adds up to the constant. If true,
that would invalidate assumptions made by scientists for basing age on
distance based on the two way speed of light.
Most physicists consider the speed of light inviolate and unchangeable.
I won't argue that case here, but you should be aware that there are
assumptions like this that are made regarding things such as the speed
of light and flow of time that are not considered in age estimates when
calculations of the age of the universe are made that can greatly impact
the calculated age if incorrect.
For more, see Jason Lisle, Does Distant Starlight Prove the Universe
Is Old?, 12/13/2007
https://answersingenesis.org/astronomy/starlight/does-distant-starlight-prove-the-universe-is-old/
back
8 NASA - WMAP - Age of the Universe
How Old is the Universe?
back
9 At least not without invoking the exotic,
hypothetical, undetectable entity known as dark matter for which there
is no evidence despite 40 years of searching for it. Prof. Carlos Frenk
states he has developed a computer simulation that generates stars and a
universe that looks like ours - but it requires you add the hypothetical
entity dark matter in a ratio of 5 to 1 with regular bayonic matter -
the visible stuff we can see:
"This is a computer simulation of the formation of the galaxy, now with invisible dark matter and gas shown here in green, About a billion years after the big bang clumps of dark matter formed, gas fell into these clumps, turned into stars but attracted by the force of dark matter - invisible dark matter gravity - these clumps came together, fused to build ever larger structures so that 10 billion years later the beautiful spiral galaxy like our own Milky Way is formed."
Prof Carlos Frenk, "Through the Wormhole with Morgan Freeman",
Episode Beyond the Darkness, TV Documentary, 2010
For more on the search for Dark Matter see:John Hartnett
- Why is Dark Matter everywhere in the cosmos, 3/31/2015
http://creation.com/why-dark-matter-everywhere
For more on dark matter and star formation see John Hartnett -
http://creation.com/stars-dont-form-naturally
10
Martin Harwit, (astronomer
and author) “Star Formation: Naissance et Enfance des Etoiles,”
Science 231 (7 March 1986):1201-1202 (ref. from:
http://creationtoday.org/everything-came-from-nothing/ accessed
10/18/2015)
back
11 NASA - WMAP - Age of the Universe
How Old is the Universe?
back
12 How could scientists know how
far a star or galaxy is from us?
http://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/30242/how-could-scientists-know-how-far-a-star-or-galaxy-is-from-us
accessed 10/15/2015
back
13 Dr. John Hartnett, Hubble, Bubble Big Bang
In Trouble, DVD, 2010
back
14
Halton C Harp, The Official Website, "Research with Fred"
(Hoyle)
http://www.haltonarp.com/articles/research_with_Fred accessed
10/19/2015
back
15 Geoffrey Burbudge, theoretical
astrophysicist 2001
Ref. from Hartnett, Hubble, Bubble
back
16 Hartnett, Hubble, Bubble
back
17 Science Fronties Online, "Venus
too Pristine" No. 73: Jan-Feb 1991
http://www.science-frontiers.com/sf073/sf073a04.htm
back
18 The evidence for Saturn's rings
being young is so powerful I devoted an entire article to it. See:
Duane Caldwell, "Saturn's
Rings are Young"
http://rationalfaith.com/2014/02/saturnsringsareyoung/
back
19 Jason Lisle, "New Horizons at Pluto"
http://www.icr.org/article/8951
back
Images
Red / Blue Shift:
Tracking Matter Around a Black Hole
NGC 7603:
Source: Halton C Arp, The Official Website, "Research with Fred"
(Hoyle)
http://www.haltonarp.com/articles/research_with_Fred
accessed 10/19/2015