 |
|
A duck dressed as a scientist is still a duck. And a pseudoscientific theory dressed up like real science is still pseudoscience. That just leaves the question: is evolution pseudoscience? Fortunately, that's an easy question to answer: yes. And even better, you don't need to be a scientist to recognize a pseudoscience, just as you don't need to be a doctor to recognize the difference between a human and a non-human like a duck. Anyone who knows what a "human" and a "duck" is can easily discern the difference. And anyone who knows what "science" and "pseudoscience" is will likewise easily discern the difference.
As you are probably already aware, a favored tactic of proponents of evolution is to label both Creation and Intelligent Design disciplines as "pseudosciences." The irony of course being that it is a trivial matter to demonstrate that Darwinian goo-to-you evolution is the epitome of a pseudoscience. Yet regardless of how clear the evidence is, you will never, ever get an evolutionist to acknowledge that Darwinian molecules-to-man evolution is a pseudoscience. So in this article we'll first take a look at how Darwinian evolution fits the definition of a pseudoscience perfectly; then press on to demonstrate how evolution breaks a number of the known laws of science further proving it to be pseudoscience in spite of their protestations that "it's science."
According to the bastion of popular secular knowledge known as Wikipedia, a pseudoscience is:
"...a claim, belief, or practice presented as scientific, but which does not adhere to the scientific method. A field, practice, or body of knowledge can reasonably be called pseudoscientific when it is presented as consistent with the norms of scientific research, but it demonstrably fails to meet these norms."[1]
So one cannot know whether something is a pseudoscience until one first understands the scientific method. Again, according to Wikipedia, the scientific method is:
"a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry is commonly based on empirical or measurable evidence subject to specific principles of reasoning. The Oxford English Dictionary defines the scientific method as "a method or
procedure that has characterized natural science since the 17th century, consisting in systematic observation, measurement, and experiment, and the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses."[2]
Evolution fits the definition of a pseudoscience
Evolution fits every criteria necessary to be identified as a pseudoscience:
Fits defintion - 1. "Presented as Scientific"
The claim that evolution is "presented as scientific" is so ubiquitous,
a defense of that statement is not at all necessary. But but to leave no
stone un-turned, I offer
this page
from the National Academy of Science that states evolution is both
science theory and fact.[3]
Fits definition - 2. "But which does not adhere to the
scientific method"
The definition of the scientific process is listed above. Below is a
nice diagram of the process:
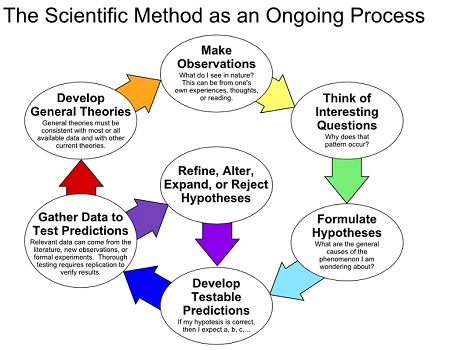
Though one is sufficient, we'll look at two places in the process where evolution fails to follow the scientific method: A. (Unable to) Make Observations; and B. (Unable to) Develop Testable Predictions
Fails Scientific Method A. (Unable to) "Make Observations"
Goo-to-you evolution fails the very first step in the process, because
it cannot be observed:
1) No one has ever observed life come from non-living molecules, cells or animals. Life always comes from life, without exception. Yet this belief (abiogenesis - which we'll return to later) is a core belief of evolutionists. Evolutionists must believe this since there simply is no other alternative once you rule out the living God as the source of all life.
And what do they substitute for observation? Bad reasoning:
The undeniable fact is that non-living materials must have formed into living materials at least once. If not through spontaneous generation, then how? [4]
Documentary: How Life began
This is common evolutionist reasoning, but it is totally flawed. It's like coming home and finding a body dead apparently from gunshot wounds, a smoking gun, and only your spouse and the family goldfish in the room - and there is gun powder residue on your spouse's hand. And from this you conclude the goldfish must have done it because you know your spouse couldn't have done it. Never mind it is impossible for your goldfish to have fired the gun, the idea of your spouse doing it is so repellent, you simply can't even seriously consider the possibility. So it is with evolutionists and God - the idea of God creating all life on earth is so repellent to evolutionists, they won't even consider it, and prefer instead to believe in the fantasy that processes that are known to be incapable of creating life, created life.
2) No one has ever observed the evolution of one type of animal to another type of animal. The change in finch beaks that Darwin observed in the Galapagos, for example, was not evolution from one kind to another. It was natural selection in operation. There's a more current example: Elephant tusks are getting smaller. Why? Because poachers are killing elephants with the bigger tusks leaving the ones with the smaller tusks to breed and reproduce.[5] So the overall effect is a population of elephants with smaller tusks. But the finches are still finches; and the elephants are still elephants, so this is not goo-to-you evolution. This is natural selection at work (well in the elephant's case it's human selection), and as I've pointed out before, natural selection is not synonymous with evolution.
Fails Scientific Method B. (Unable to) "Develop Testable
Predictions"
Honest evolutionists acknowledge the inability for evolution to meet the
scientific requirement of being predictive in a manner that is testable:
"The theory is inadequate because it is not predictive. It explains what has evolved, but not what will. There are too many possible courses evolution can take."[6]
Professor Armand Marie Leroi
Imperial College, London
How true - too many paths - leaving
room for plenty of stories. So while
they can't make a scientific prediction, they can indulge their wild
flights of fancy. So if you've got a animal and you're looking for
their origin, evolutionists have a story for you. Based on two
populations of fish in two separate lakes that look similar, Prof. Leroi "hopes" evolutionists can make predictions in the future[7].
Like other evolutionary hopes and dreams this one will remain
unfulfilled since evolution of the type I'm discussing is impossible.
Fits Definition 3. (Fails to meet) The norms of
scientific research.
This is a broad topic, and cannot be covered in any detail here. But a
recurring area of concern here that should never happen in research is
the fabrication or falsification of data. Not only is it
unethical as was universally agreed in a recent survey[8], and tends to
make evolution look like the pseudoscience that it is; but more
importantly if evolution is so obvious, and there is so much evidence
for it, why has there been, and continues to be so much fraud,
fabrication and falsification of data in attempts to prove it true? To
see some examples of the frauds, just search
thecreationclub.com for "Frauds of
Evolution."
So there you have it. Evolution clearly meets the definition of a pseudoscience. And you know the old saying - if it looks like a duck, walks like a duck and quacks like a duck, it's a duck. And so it is with evolution. It may be dressed up as science, but it's really pseudoscience. But the above demonstration that evolution fits the definition of a pseudoscience to a T is really just an introduction to what I believe the stronger evidence is that demonstrates it's a pseudoscience: evolution is a pseudoscience because it breaks the known laws of science.
Pseudosciences break known laws of science
In an article titled Is Evolution Pseudoscience Mark Johansen, a CMI author considers this proposition and goes through a 10 point list from the Skeptics Dictionary that identifies pseudosciences and shows how evolution meets 9 of the 10 criteria. Item number 9 is of particular interest:
"Some pseudoscientific theories … contradict known scientific laws and use ad hoc hypotheses to explain their belief."[9]
Evolutionists are fond of calling evolution "science" and "fact" but real science does not contradict the established laws of science. With evolution breaking so many laws of science, you can call evolution pseudoscience, or religion. But what you can't call it, is science. It fits neither the definition of science, nor the method of science (as shown above0, nor follows the laws of science (as shown below). So without further ado, some of the many laws of science that evolution breaks.
1. Evolution breaks the law of
Biogenesis.
The law of biogenesis states that life comes only from life. That is all
that has ever been observed. Life from Non-living things has never been
observed. The idea of "spontaneous generation" was decisively destroyed
in the 19th century with Louis Pasteur's swan necked flask experiment.
But in the 19th century, the idea of spontaneous generation concerned
mice coming from dirty rags and wheat instead of the current chemical
evolution variety of life coming from replicating molecules. With that
as the case, evolutionists think they've distanced themselves from the
concept. In fact popular Cosmos host Neil deGrasse Tyson pokes
fun at the concept and the foolishness of spontaneous generation:
"I always liked the spontaneous generation concept - some dirty rags, some wheat, look the other way and mice crawl out. That's kind of fun. I don't know why that concept hung on for so long. Because a simple test could have verified that mice do not spontaneously generate themselves out of dirty clothes and wheat."[10]
Neil deGrasse Tyson
True, scientists no longer believe in "spontaneous generation" of the type they spoke of in the 19th century. Now they believe in "abiogenesis," a theory of life arising through chemical evolution - but it has the same problem: it still requires life to come from lifeless matter - a ludicrous proposition. The list of reasons of why chemical evolution is impossible is extensive and far beyond the scope of this article. So I can't cover them here. (Though you can see one of the reasons in my previous article here on the impossibility of evolution to produce a protein.) Let me suffice it by giving you the bottom line:
"The idea of the origin of life by natural processes is a preposterous idea. Absolutely preposterous idea."[11]
Don Batten
Agricultural Scientist and Creationist
"For evolutionists to believe in chemical evolution, this is not a position they got from science, but a position they got from blind faith. They're basically having to believe in miracles because it's not real chemistry there they can appeal to."[12]
Jonathan Sarfarti
Physical Chemist, Spectroscopist and Creationist
2. Evolution contradicts Genetic
processes.
Once again I will limit myself to just two of the many areas of genetics
where evolutionary processes contradict known genetic processes.
A) Evolution with it's trial and error method over millions of years
predicts that there will be much "junk" found in the code of DNA. Some
evolutionists state that up to 98% of our DNA is junk. But scientists
have learned how seriously mistaken that view is. Protein coding is one
of the main functions of DNA. But there are parts of DNA that don't code
for proteins, and it's those areas that evolutionists have called
"junk." But with further research, scientists have
learned that the non-protein coding portions of DNA formerly
considered "junk" by some are performing a number of other
critical cellular functions. And in fact, "It's now known that parts of
genome code for more than 1 thing at the same time." [13]
In other words, there are messages within other messages of DNA strings. Such double coding
or multiple coding - if you
will - is a mark of extreme intelligence as I pointed out in
DNA and Windtalkers. Further,
"Overlapping codes are almost impossible to improve upon - because if you improve on one of the codes you are destroying or disrupting one of the other codes."[14]
John Sanford
Thus the concept of "junk DNA" is, as plant geneticist John Sanford states: " ...profoundly wrong and will be recorded in history as one of the "greatest blunders in science." [15]
B) Evolution states that random mutation and natural selection can emulate the process of design to get ever more complex creatures until you get the diversity of creatures we see today. Yet the mutations in the human genome are destroying good design, not adding new information, or features. The human genome is suffering from genetic entropy, and evolution can do nothing to stop it. The result:
"So genetic entropy is profound...It is lethal to genetic evolutionary theory - it means things are going down, not up."[16]
John Sanford
Once again evolution predicts the exact opposite of what the physical reality is.
3. Evolution breaks the Laws of Chemistry
Many suggestions from evolutionists for the first living cells have them emerging from some primordial ooze or soup. But that theory is seriously flawed. Because for life, you need to build many large molecules from small ones. The problem is - the chemistry of molecules doesn't work that way. The normal process is large molecules are regularly broken down to smaller ones; not smaller ones joined together to get larger ones:
"Everything I've learned about real chemistry shows that reactions go in the opposite way from what's required for life to come from non living chemicals - breaking up large molecules to small molecules."[17]
Jonathan Sarfati
And with regard to the primordial soup:
"Any chemist wouldn't have water in the reaction because water tends to drive the reaction in the opposite direction towards the little molecules.
Yet the primordial soup would have inevitably had loads of water in it, so it's the last place a real chemist would try to make proteins or DNA."[18]
Jonathan Sarfati
Chalk up another huge fail for evolution with regards to any chance of building the necessary chemical building blocks for life while abiding by the laws of chemistry.
4. Evolution breaks the Laws of Information Theory
Philosophical materialist scientists (those who believe only material things exist) used to believe that reality consisted only of matter and energy - which are - as Einstein revealed to the world, different manifestations of the same thing. But in these latter days, scientists have had to acknowledge that there is a non-material portion that comprises reality - information:
"During the 19th century scientist believed there were two fundamental entities - matter and energy. But as we enter the 21st century there's a third fundamental entity that science has had to recognize and that is information."[19]
Stephen Meyer
Philosopher of Science
Even evolutionists recognize that DNA contains information. The information is in fact coded information. Further, as noted above, it is coded with overlapping information making it information packaged in a highly complex manner . The question that Darwinists can't answer, is what is the origin of the information in DNA and wherever else information is found in living creatures? And what is the origin of the highly complex information storage and retrieval system we call DNA? We know two things about the origin of information: 1. Natural processes cannot create information. 2. Intelligent agents can produce information:
"So at present there is no naturalistic explanation, no natural cause that produces information. Not natural selection, not self organizational processes, not pure chance.
But we do know of a cause which is capable of producing information, and that is intelligence."[20]
Stephen Meyer
Darwinist say that mutations and natural selection can create information, but as Meyer points out they cannot. Mutations destroy information, and natural selection can only eliminate information. Evolutionists need a naturalistic way to create information, but there is none. Information comes only from agents with intelligence. This is such a serious challenge to evolution that Meyer characterized the problem this way:
"Neo-Darwinism and its associated theories of chemical evolution and the like will not be able to survive the biology of the information age, the biology of the 21st century."[21]
Stephen Meyer
5. Evolution breaks Darwin's own slow, gradual process maxim
This next item is included not because it is science, but because it
demonstrates that not only does evolution not follow the laws of science
it doesn't even follow its own laws. Punctuated Equilibrium is an update to evolutionary theory proposed
in 1972 by noted paleontologists Niles Eldredge and Stephen Jay Gould.
It was proposed because evolutionists realized the fossil record does
not conform to Darwin's theory of slow, gradual change of species.
As Wikipedia explains it, the fossil record of an evolutionary
progression:
"...typically consists of species that suddenly appear, and ultimately disappear, in many cases close to a million years later, without any change in external appearance."[22]
Eldredge and Gould were among the evolutionists who realized the evidence simply doesn't fit Darwin's theory, and instead of discarding the theory, changed it to allow what Darwin said was forbidden: saltations - or jumps in the fossil record. But as evolution evangelist Richard Dawkins acknowledges:
"Without Gradualness.. we are back to a miracle."[23]
Evolutionists like to pretend they believe in Darwin's theory of slow and gradual change, but the fact that punctuated equilibrium was even proposed shows that 1.) The fossil record doesn't support Darwin's theory, and 2.) Evolutionists have conceded that slow gradual processes simply cannot do what they claim they can, and that in fact the only solution is something that can produce saltations - jumps. But jumps require the intervention of an agent outside of the material world; something that can intelligently manipulate natural processes to do what slow and steady processes can't - to do what Dawkins correctly characterized as "a miracle."
Conclusion
This is not intended to be an exhaustive list of all the laws of science
broken by evolutionary theory, but merely one sufficient to show that
that Darwinian evolution does in fact break many laws of science
and in fact breaks its own scientific requirements and therefore is rightfully characterized as a pseudoscience.
Marine biologist Robert Carter summarizes it succinctly:
"Everything we know about the laws of chemistry, genetics, statistics and information theory argues against any life from non-life idea. But an evolutionist must believe that scientific laws are violated for life to arise from none living chemicals. That sounds like faith to me."[24]
Robert Carter
So you can legitimately call evolution pseudoscience, or you could call it religion. But if you know anything about the operation of science in the real world, and how Darwinists state evolution operates, you cannot call evolution science.
Duane Caldwell | 5/5 /2016
Follow @duanecaldwellNotes
1. Pseudoscience, Wikipedia, accessed
5/1/2016
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pseudoscience
Back
2. Scientific Method, Wikipedia,
accessed 5/1/2016
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scientific_method
Back
3. Evolution Resources: Is Evolution
Theory or Fact, The National Academy of Sciences, accessed 5/1/2016,
http://www.nas.edu/evolution/TheoryOrFact.html
Back
4. How Life Began, History Channel
Documentary, 2008
Back
5.
Richard Gray, "Why elephants are not so long in the tusk",
The Telegrah, Jan 20, 2008,
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/science/science-news/3322455/Why-elephants-are-not-so-long-in-the-tusk.html
Back
6. Professor Armand Marie Leroi, What
Darwin Didn't Know, BBC documentary, 2009
Back
7. Keep in mind Leroi makes the classic
evolutionist mistake - he assumes similar features are due to common
evolutionary paths instead of a common designer.
Back
8. Evaluation of the Research Norms of
Scientists and Administrators Responsible for Academic Research
Integrity (Abstract), Stanley G. Korenman, MD; Richard Berk, PhD;
Neil S. Wenger, MD; Vivian Lew, PhD; JAMA. 1998;279(1):41-47.
doi:10.1001/jama.279.1.41.;
http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=185891
Back
9. Mark Johansen, Is Evolution
Pseudoscience?, Creation Ministries International, Magazine article:
Creation 29(4):25–27 September 2007; Online:
http://creation.com/is-evolution-pseudoscience
Back
10. Neil deGrasse Tyson, How Life Began,
History Channel Documentary, 2008
Back
11. Don Batten, Evolution's Achilles Heel,
Creation Ministries International Documentary DVD, 2014
Back
12. Jonathan Sarfati, Evolution's
Achilles Heel
Back
13. Rob Carter
Evolution's Achilles Heel
Back
14. John Sanford, Evolution's Achilles Heel
Back
15. John Sanford, Evolution's Achilles
Heel
Back
16. John
Sanford, Evolution's Achilles Heel
Back
17. Jonathan Sarfati, Evolution's
Achilles Heel
Back
18.
Jonathan Sarfati, Evolution's Achilles Heel
Back
19. Stephen Meyer, Unlocking the Mystery of
life, Illustra Media Documentary (DVD), 2002
Back
20. Stephen
Meyer, Unlocking the Mystery of life
Back
21. Stephen Meyer, The Case for
a Creator, Illustra Media Documentary (DVD), 2006
Back
22. Punctuated
Equilibrium, Wikipedia, accessed 5/2/2016,
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Punctuated_equilibrium
Back
23. Richard Dawkins,
referenced from Darwin's Dilemma:
The Mystery of the Cambrian Fossil Record, Illustra Media
Documentary (DVD), 2009
Back
24. Robert Carter, Evolution's
Achilles Heel
Back
Images:
Featured Image: duck/lab © Jeffrey Collingwood / fotolia ; © apinan /
fotolia respectively
Scientific Method: By ArchonMagnus (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)],
via Wikimedia Commons