Christians are often accused of believing the unbelievable. One of those “unbelievables” is the claim that the universe was created in 6 days. But is that really unbelievable? Even if it were, are Christians the only ones who believe something that’s unbelievable? Consider this: physicists also believe something once considered unbelievable. If that is true, perhaps the belief of Christians is not as wild and crazy as some think.
Physics and the Unbelievable
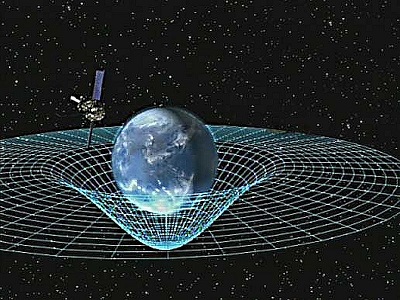
Consider the well known phenomenon of gravity. Since Newton published his theory of gravity in the seventeenth century, people have believed in the pull exerted by the force of gravity. Newton is widely credited with being the founder of modern science based on his law of gravity and laws of motion. Newton’s understanding of gravity seems intuitive – of course things are pulled by the force of gravity. Yet scientists today don’t believe his model of gravity. They say that force is not real; it’s something Newton just made up. There is no pull of gravity.
Which leaves those of us who were taught Newton’s theory of gravity as an unchanging “law” of science in a bit of a quandary. We are now told not to believe in a foundational theory of science given to us by the father of modern science. Saying Newton was wrong was once considered unthinkable, much less believable. Yet that is precisely what scientists today are asking us to do. Do you believe them? If you do, you too believe a number of things once considered nonsense by modern scientists as demonstrated below. And if you don’t you’re at odds with modern science. Continue Reading