Side bar article to: Fairytale Apologetics, the Doctrine of Demons and Biblical Inerrancy
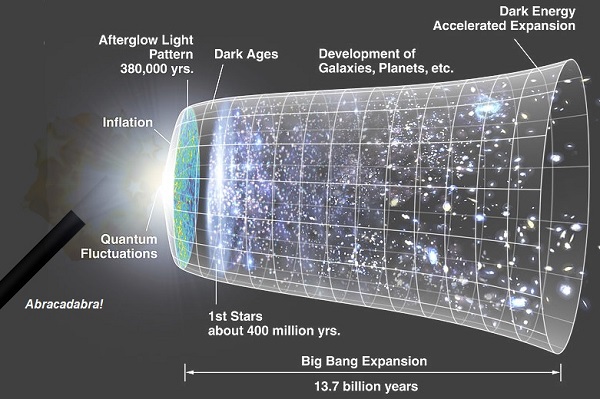
There are quite a number of problems with the Big Bang theory – any one of which without a feasible solution – is enough to falsify the theory. Search for “Big bang problems” and you’ll find lists with item counts ranging from 3 to 30. Here, as a quick reference, is a list of 10 (more or less) well known, and insurmountable problems with the big bang theory. Continue Reading



